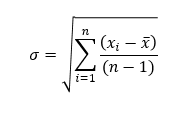Home / Statistical Tools / Distribution Fit/Calc / Distribution Fit / Normal Distribution
Normal Distribution¶
Distribution Fitting: Non-Reliability¶
From Excel click...
QXL Stat Tools Tab > Distribution Fit/Calc > Distribution Fit > 2-Param Normal
Distribution Fitting: Reliability¶
From Excel click...
QXL Stat Tools Tab > Reliability > Uncensored > 2-Param Normal
Probability Calculator¶
From Excel click...
QXL Stat Tools Tab > Distribution Fit/Calc > Distribution Calculator > Normal
The Normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution named for Carl Friedrich Gauss. It is also referred to as Gaussian Distribution, Law of Error, Laplace's Second Law, and Gaussian Law. Most authors give credit to De Moivre with significant contributions from Gauss and Laplace. In particular, Gauss's 1809 monograph introduced the method of least squares, method of maximum likelihood, and the Normal distribution. The term "Normal" was likely introduced by Gauss himself; however his meaning was "orthogonal" rather than "usual". Pearson popularized the term "Normal" in the early 20th century.
The Normal distribution has two parameters, the mean and standard deviation. The term "Standard Normal", coined by Hoel in 1947, refers to a Normal Distribution with Mean=0 and Sigma=1.
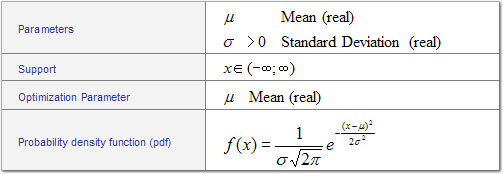
Unlike most distributions, the maximum likelihood estimates for the mean and standard deviation are available in closed form (non-iterative) solution. The mean is simply the arithmetic average of the dataset. However, the standard deviation can come in two forms, unbiased and biased.
Biased Standard Deviation -- Population Standard Deviation¶
Some statisticians would take issue with the biased standard deviation being equated with the population standard deviation. For purposes of equivalency with Excel, we present them in this way. However, the more technically correct term for the equation below would be the biased standard deviation or the standard deviation without Bessel's correction. When using the normal distribution for reliability analysis, by convention the population standard deviation (biased) is used instead of the sample.
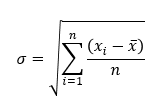
Unbiased Standard Deviation -- Sample Standard Deviation¶
The unbiased standard deviation replaces n in the denominator with n-1. This correction was proposed by Bessel and is often called Bessel's correction. Numerous articles have been written about the correction from the perspective of degrees of freedom and expected value theory. For more information, search "Bessel's Correction" on the internet.