Home / Statistical Tools / Distribution Fit/Calc / Distribution Calculator / Discrete Distribution Overview
Discrete Distribution Overview¶
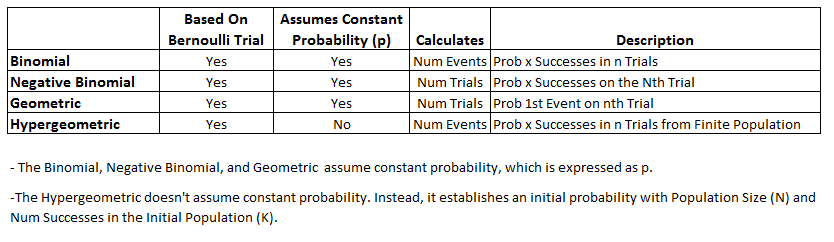
The Binomial, Negative Binomial, Geometric, and Hypergeometric are all based on Bernoulli trials. The table below is an overview of differences.
Bernoulli¶
Link To Help Topic: Bernoulli
Purpose: Calculate probabilities associated with a Bernoulli trial. A Bernoulli trial has two possible outcomes, usually expressed as "Success" and "Failure".
Example: If we define a "heads" as a success from a single random coin flip, we can model the probability of success from a single flip using the Bernoulli trial.
Notes: As a calculator, the Bernoulli distribution isn't that useful. However, it is the foundation for the Binomial, Geometric, and Hypergeometric which are based on multiple Bernoulli trials.
Binomial¶
Link To Help Topic: Binomial Distribution
Based on Bernoulli Trial: Yes
Purpose: Calculate probabilities for n draws, each with probability p, from an infinite population.
Example: If a coin is flipped 25 times, what is the probability it comes up heads exact 12 times?
Notes: If the sample size isn't infinite, then use the Hypergeometric Distribution.
Negative Binomial¶
Link To Help Topic: Negative Binomial Distribution
Based on Bernoulli Trial: Yes
Purpose: Negative Binomial returns the probability of observing x failures and r successes with success on the last trial.
Example: If a coin is repeatedly tossed, what is the probability the second heads occurs on the 7th toss?
Geometric¶
Link To Help Topic: Geometric Distribution
Based on Bernoulli Trial: Yes
Purpose: The Geometric distribution provides the probability of observing x trials before the first success from multiple Bernoulli trials.
Example: If a coin is repeatedly flipped, what is the probability that the first head will occur on the 4th toss?
Notes: If the population isn't infinite, use the Hypergeometric distribution.
Hypergeometric¶
Link To Help Topic: Hypergeometric Distribution
Based on Bernoulli Trial: Yes
Purpose: Calculate the probability of x success in n draws without replacement from a finite population of size N containing K successes.
Example: Calculate the probability of drawing 3 hearts in a hand of five cards from a standard deck of 52 cards.
Notes: The Hypergeometric distribution is related to the Binomial. Where the Binomial distribution assumes an infinite population (or draws with replacement), the Hypergeometric can handle the changing probability with each draw.
Uniform Discrete¶
Link To Help Topic: Uniform Discrete Distribution
Based on Bernoulli Trial: No
Purpose: Each outcome between the lower and upper bounds are equally likely.
Example: When drawing one card from a deck, each suit is equally likely. The probability of drawing a Heart, Spade, Diamond, or Club is equal.
Poisson¶
Link To Help Topic: Poisson Distribution
Purpose: The Poisson distribution is used to calculate the probability of a number of events occurring based upon the probability of a single event.
Example: The rate of occurrence of hurricanes in Central Florida is 17.5% per year. Using the Poisson distribution, we can calculate the probability of having four hurricanes in a single year.
Notes: The Poisson distribution can be used on non-integer sample sizes. For example, we could change 17.5% per 365 days into 8.75% per 182.5 days (half a year).