Home / Statistical Tools / Distribution Fit/Calc / Distribution Calculator / Negative Binomial Distribution
Negative Binomial Distribution¶
Probability Calculator¶
From Excel click...
QXL Stat Tools Tab > Distribution Fit/Calc > Distribution Calculator > Negative Binomial
The Negative Binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution. It can be used with two mutually exclusive outcomes of a Bernoulli trial, typically labeled "Success" and "Failure". The negative binomial has two parameters. p is the probability of success in a single Bernoulli trial. r is the number of successes before the experiment is terminated. The Negative Binomial returns the probability of observing x trials before the threshold number of successes (r).
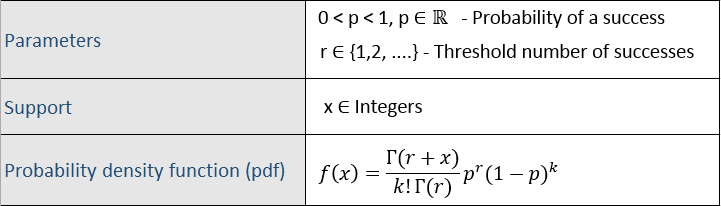
Notes:
The Geometric Distribution is a special case where r = 1.
The Poison distribution is related to the Negative Binomial where r approaches infinity.
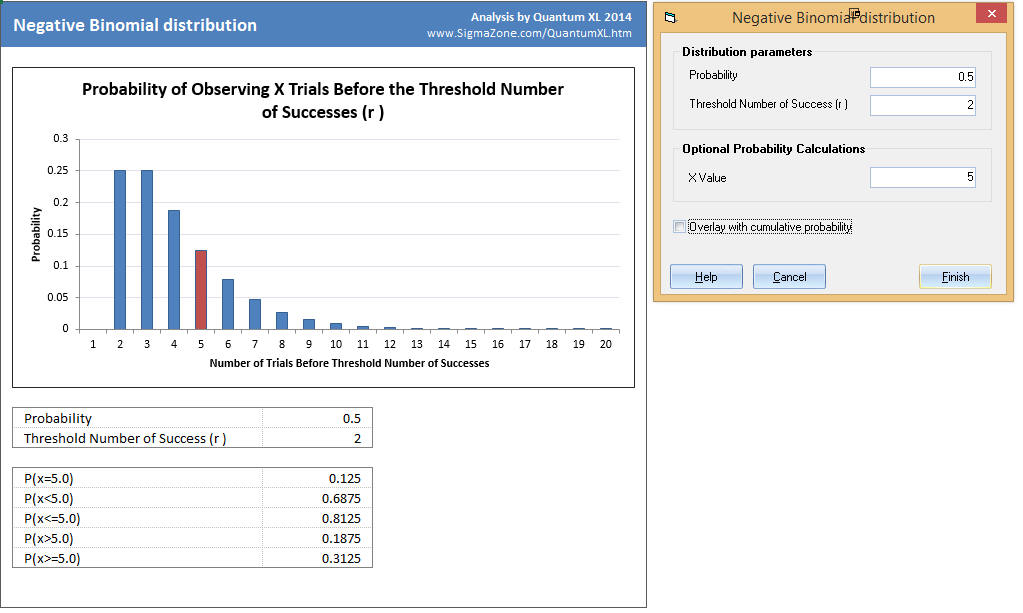
Example
You would like to know the probability of flipping heads 2 times in 5 attempts.
p = .5 (probability of heads)
Threshold Number of Successes = 2 (Two heads)
X Value = 5 (5 attempts)
The analysis from Quantum XL is below.
-
The bar when X=1 is zero. Since we need 2 successes (heads) it isn't possible to obtain two heads in a single flip. Therefore, the bar has a probability = 0.
-
The bar when X=2, represents the probability of flipping heads two times in two flips (two successes in a row). The probability of that occurring is .25.
-
P(X<=5) is the probability of seeing at least two heads in 5 flips. The probability is 81.25%.
-
P(X=5) is the probability of seeing the second head on the 5th flip (exactly the 5th flip, not before or after).
-
If you sum the bars for X=1, X=2, X=3, X=4, and X=5 then it will equal P(X<=5).